
Skin Cancer is the most common form of cancer and should not be ignored.
Basal Cell is the predominant form of skin cancer and squamous cell is the second most widespread. Actinic keratosis is a common and treatable pre-cancer skin lesion affecting more than 58 million Americans.
According to the American Cancer Society 87,000 new melanoma cases will be diagnosed this year.
While melanoma isn’t the most prevalent skin cancer it is the deadliest cancer. In 2017, close to 10,000 deaths will occur due to melanoma
Melanoma is most typical in older white males and young adult women; however, it can occur throughout all demographic groups. Melanoma is survivable if caught early. The survival rate of melanoma is only 15-20 percent in advanced disease.
What is the best way to prevent skin cancer?
While we can do our best to prevent skin cancer, sun exposure is inevitable. Here are some precautions you can take to help prevent skin cancer: Seek the shade, especially between 10 A.M. and 4 P.M.
- Do not let yourself burn.
- Avoid tanning in UV tanning booths.
- Cover up with clothing, including a broad-brimmed hat and UV-blocking sunglasses.
- Use a broad spectrum (UVA/UVB) sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher every day. For extended outdoor activity, use a water-resistant, broad spectrum (UVA/UVB) sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
- Apply 1 ounce (2 tablespoons) of sunscreen to your entire body 30 minutes before going outside.
- Reapply sunscreen every two hours or immediately after swimming or excessive sweating.
- Keep newborns out of the sun. Sunscreens should only be used on babies over the age of six months.
- Examine your skin head-to-toe every month.
- See your physician every year for a professional skin exam.
What about getting enough Vitamin D?
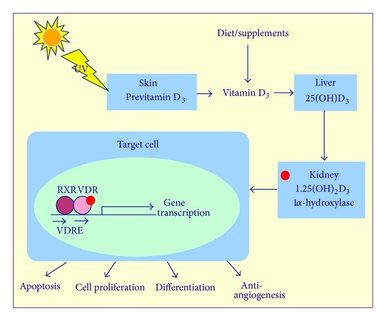
One of the ways we receive vitamin D is from the sun. Vitamin D is good for our bones and our immune system. Vitamin D3 is produced in the body after the skin has absorbed the cholecalciferol from UVB rays. UVB doesn’t just stimulate our Vitamin D levels it also damages the skin. The more overhead the sun, the stronger and more damaging the UVB rays are.
The other way to get vitamin D is by supplementation. The argument that the only way to get our Vitamin D is through sunlight is not true.
Spending time in tanning booths is not the way to get Vitamin D. Tanning beds increase the risk of skin cancer and at the very least damages our skin.
Since Vitamin D production and sun damage go together, the same UVB rays needed for us to produce vitamin D also causes changes in our DNA and premature aging. If you want to produce the vitamin D from the sun, do so get and get out in as little time as possible. If at high noon, as little as ten minutes is sufficient. It is best to have your face and neck covered and your torso exposed but this may be impractical so as much body surface as possible.
What are some of the signs of Skin Cancer?
- Any change on the skin, especially in the size or color of a mole or other darkly pigmented growth or spot, or a new growth
- Scaliness, oozing, bleeding, or change in the appearance of a bump or nodule
- The spread of pigmentation(color) beyond its border, such as dark coloring that spreads past the edge of a mole or mark
- A change in sensation, itchiness, tenderness, or pain
Resources
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/skin-cancer.html
ISRN Oncol. 2013; 2013: 483687. 2013 Feb 26. doi: 10.1155/2013/483687
Vitamin D: Are We Ready to Supplement for Breast Cancer Prevention and Treatment?
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed